Artificial Intelligence (commonly abbreviated to AI) directly from the Oxford English Dictionary: "The capacity of computers or other machines to exhibit or simulate intelligent behavior; the field of study concerned with this. In later use also: software used to perform tasks or produce output previously thought to require human intelligence, esp. by using machine learning to extrapolate from large collections of data. Also as a count noun: an instance of this type of software; a (notional) entity exhibiting such intelligence."
Chatbots like ChatGPT are how a lot of people conceptualize AI, but AI has been part of our digital experience for a years. Voice assistants, GPS map systems, and content recommendation algorithms are all popular examples of AI.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
According to the Oxford English Dictionary: in mathematics and computing, an algorithm is "a procedure or set of rules used in calculation and problem-solving; (in later use spec.) a precisely defined set of mathematical or logical operations for the performance of a particular task."
Rule-based modeling of human language that allows AI to understand and respond in a natural language.
A mathematical framework of various algorithms trained on data to recognize patterns, make predictions, or perform specific tasks. It processes inputs, generate outputs, and improves its performance through training on data sets.
Narrow AI Also known as: Weak AI
AI capable of performing specific tasks. Narrow AI uses learning algorithms and training data such as open-access content, user input, and other curated data to develop its capacity to provide accurate output.
Examples of narrow AI
AI's capability to learn from data using algorithms, enabling them to identify patterns and make decisions or predictions without being explicitly programmed for each task. In other words, machine learning allows AI to improve performance on a task over time by learning from examples rather than relying on hard-coded instructions.
A multilayered model inspired by the functions of biological neurons (i.e. the human brain). It consists of layers of nodes (neurons) that process inputs through weighted connections. These weights adapt by training on data sets to optimize the model's ability to recognize patterns and make predictions.
A subset of machine learning that uses artificial neural networks to learn from massive amounts of data. It can handle both structured and unstructured data, discovering patterns and features without needing explicit instructions. Deep learning enables AI to perform complex tasks like image recognition, natural language understanding, and speech generation with increasing accuracy as they are exposed to more data.
AI that is capable of producing output like text, images, audio, or video based on user input (prompts). Generative AI is proficient at recognizing patterns and predicting coherent responses and uses machine learning to extrapolate from large datasets. Commonly used generative AI includes chatbots like ChatGPT, Gemini, and CoPilot.
A type of model trained on massive amounts of text data. It learns patterns, structures, and relationships in language to process inputs and generate outputs in natural language. LLMs can perform tasks such as answering questions, summarizing information, writing content, or translating text without being explicitly programmed for each specific task.
Artificial General Intelligence Also known as: Strong AI
Artificial General Intelligence currently only exists in theory. This type of AI would have the capacity to rival human intelligence, solve problems, and learn all without human intervention. Artificial General Intelligence would be able to excel at performing a variety of tasks (as opposed to Narrow AI).
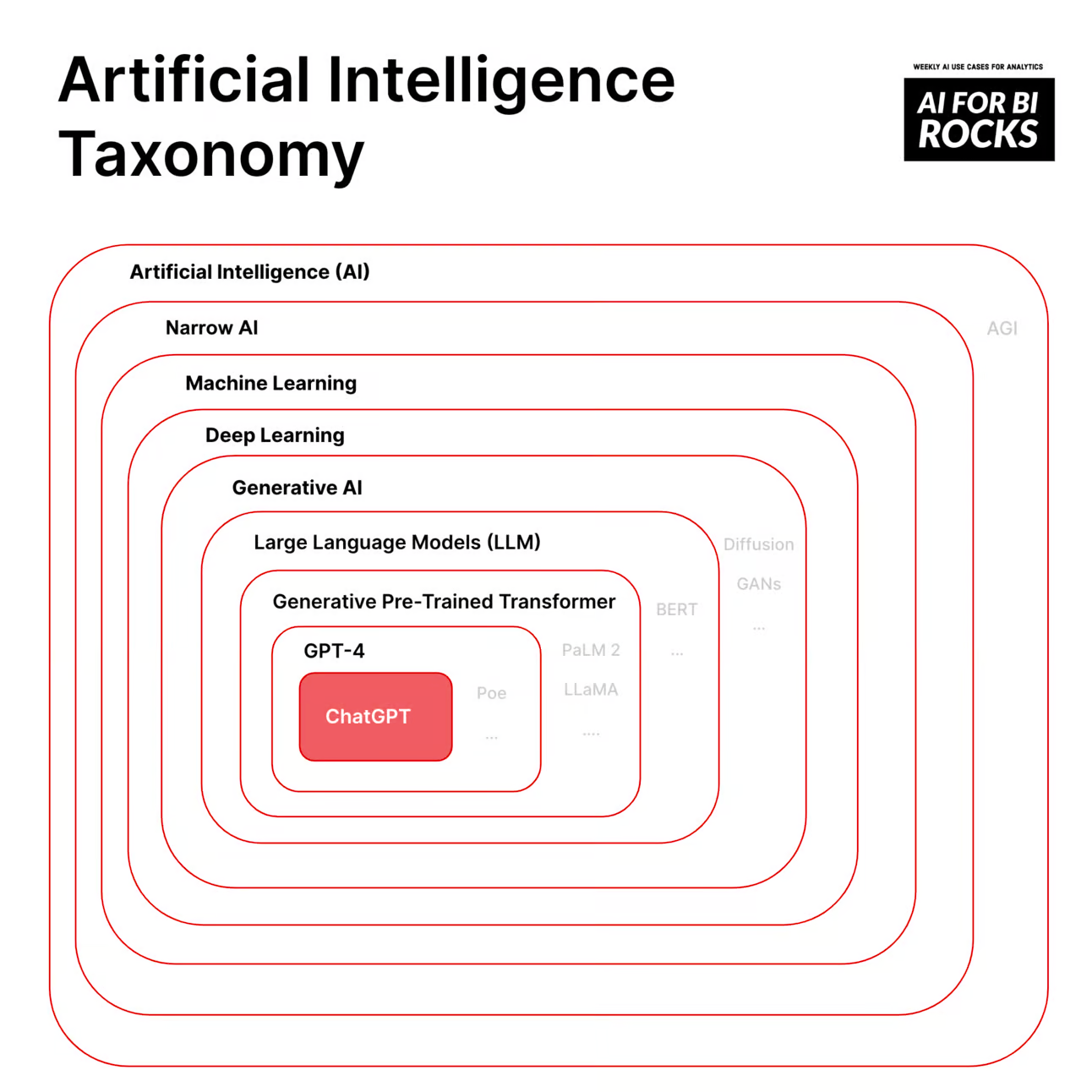
Artificial Intelligence Taxonomy by Tobias Zwingmann. Originally published with AI For BI Rocks.